- Top Results
- Bosch Sensortec Community
- Learn
- Knowledge base
- BMP series pressure sensor design guide
BMP series pressure sensor design guide
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Selecting the right part
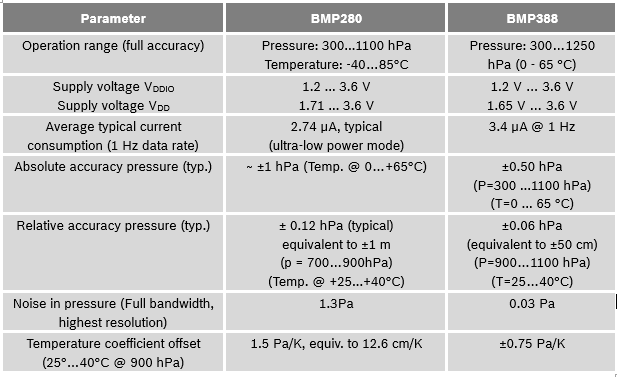
The BMP series of pressure sensor contains 2 products: BMP280 and BMP388. Table 1 shows an overview of the features.
Table 1: Overview of the products in this family
Key features
- LGA with metal lid package
- SPI or I2C interface
- Built-in IIR filter.
Differences between products
The main differences in the BMP product family are in the thickness of the package, and the overall performance of the MEMS element. BMP388 offers higher performance in a smaller package compared to BMP280. See the complete list of differences in Table 2.
Table 2: Differences between BMP product family members
Available evaluation tools and software
To best to evaluate the products from the BMP family, we recommend the following combination of evaluation tools:
- COINES Desktop software (Windows version &Linux version & MacOS)
- Development Desktop Software
- Application board 2.0
- BMP280 shuttle board
- BMP388 shuttle board
Reference design
Figure 1 shows a complete schematic of a typical use case.
BMP280
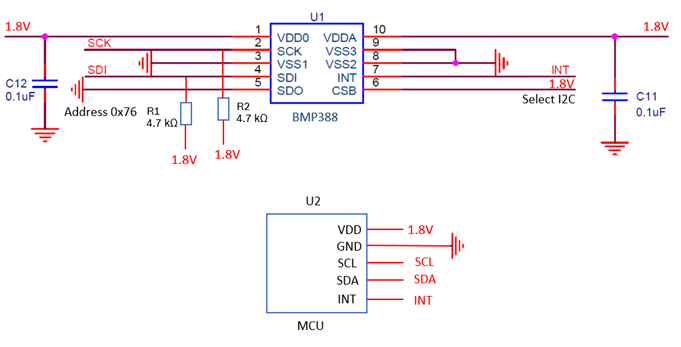
Figure 1: Exemplary Reference design
Bill of materials
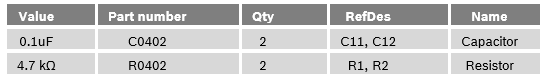 Table 3: Bill of materials
Table 3: Bill of materials
Layout recommendations
Because the BMP sensor family contains tiny mechanical structure inside the package, care must be taken during the layout phase to ensure the best performance. The complete handling and soldering guide can be found on the Bosch Sensortec’s website.
BMP28x Handling, soldering & mounting instructions
BMP380 Handling,soldering & mounting instructions
In addition to the attached guidelines, see below for the typical manufacturing procedure for the BMP388 pressure sensor.
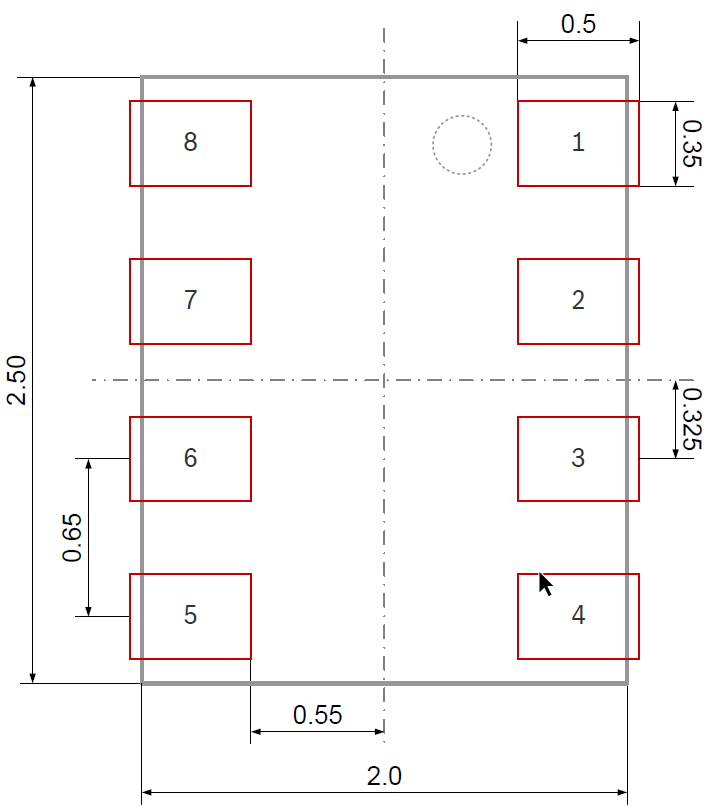
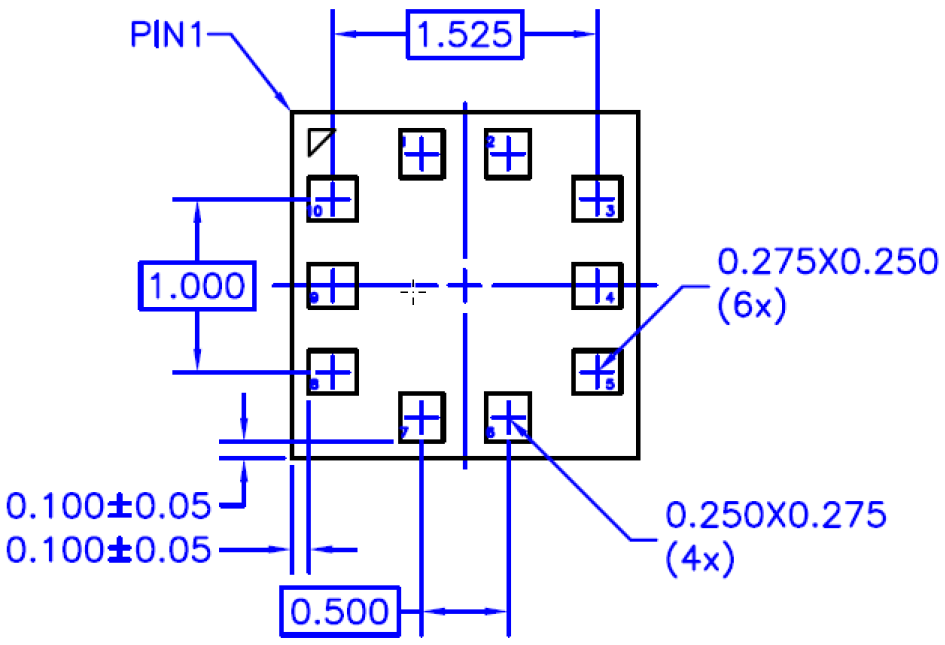
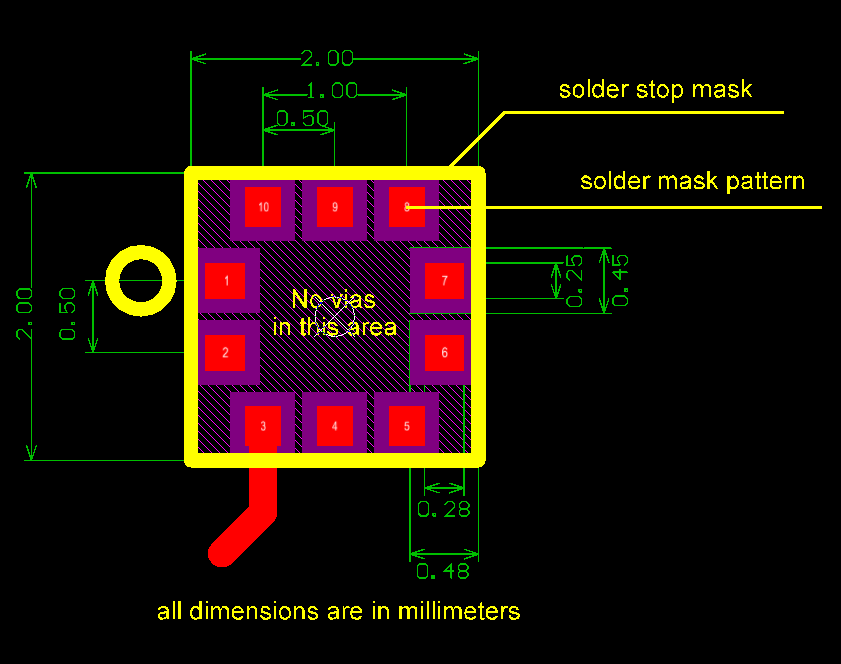
Landing Pattern
BMP280
BMP388
Figure 2: Recommended landing pattern
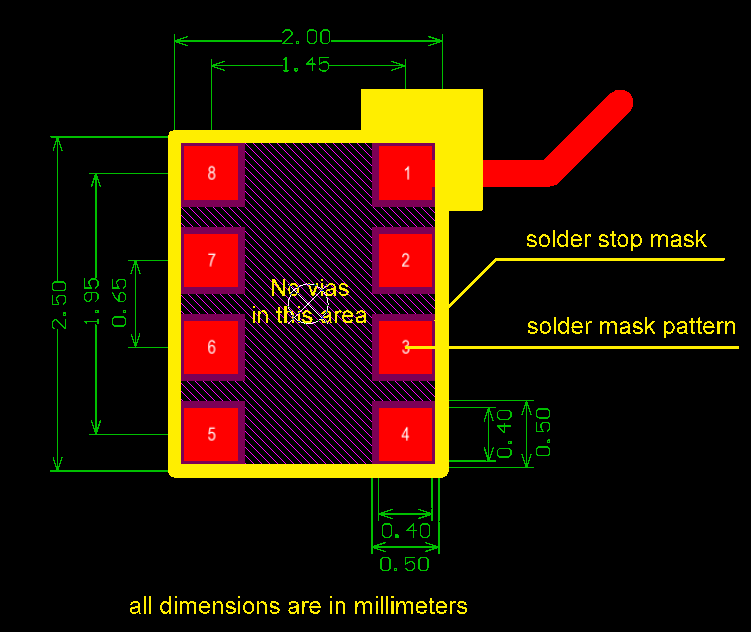
Typical Layout
BMP280
BMP388
Figure 3: Typical layout
Manufacturing notes
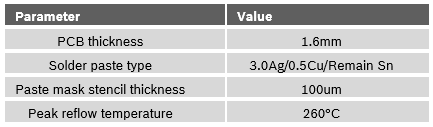 Table 4: Manufacture recommendation
Table 4: Manufacture recommendation
First power-on
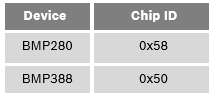
After powering on the sensor for the first time, the initial specs would be tested for communication with the device. This can be done simply by reading the chip identification code in the register 0xD0 (BMP280) 0x00 (BMP388). See below for the expected values:
Table 5: Chip IDs of the BMP product family
Here is some sample code on how to perform this test, based on the BMP388 , using the COINES software as the host.
/*!
* @brief This internal API is used to check the bmp388 sensor chip ID
*
* @param[in] void
*
* @return void
*
*/
static void init_bmp3(void)
{
int8_t rslt;
rslt = bmp3_init(&bmp3Dev);
if (rslt == BMP3_OK)
{
printf("BMP3 Initialization Success!\n");
printf("Chip ID 0x%X\n", bmp3Dev.chip_id);
}
else
{
printf("Chip Initialization failure !\n");
exit(COINES_E_FAILURE);
}
}How to read sensor data
Here is some sample code on how to read sensor data, based on the BMP388, using the COINES software as the host
/*!
* @brief This internal API is used to read the streaming data in a while loop and
* print in console.
*
* @param[in] void
*
* @return void
*/
static void read_sensor_data(void)
{
int times_to_read = 0;
while (times_to_read < 200)
{
bmp3_get_sensor_data(BMP3_ALL, &bmp3_comp_data, &bmp3Dev);
printf("T: %.2f, P: %.2f \n", (bmp3_comp_data.temperature / 100.), (bmp3_comp_data.pressure / 100.));
fflush(stdout);
coines_delay_msec(10);
times_to_read = times_to_read + 1;
}
}Sample code
The complete sample code shown above can be compiled and executed from the COINES installation directory (by default, C:/COINES under Windows), from the following subfolder: \examples\c\bmp3
Usage
The COINES installation provides sample code on how to turn on the sensor, configure it and read out the pressure data. COINES\v1.0\examples\c\bmp3
Sample code
/*!
* @brief Main Function where the execution getting started to test the code.
*
* @param[in] argc
* @param[in] argv
*
* @return status
*
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int16_t rslt;
struct coines_board_info board_info;
init_bmp3_sensor_driver_interface();
rslt = coines_open_comm_intf(COINES_COMM_INTF_USB);
if (rslt < 0)
{
printf("\n Unable to connect with Application Board ! \n"
" 1. Check if the board is connected and powered on. \n"
" 2. Check if Application Board USB driver is installed. \n"
" 3. Check if board is in use by another application. (Insufficient permissions to access USB) \n");
exit(rslt);
}
rslt = coines_get_board_info(&board_info);
if (rslt == COINES_SUCCESS)
{
if (board_info.shuttle_id != BMP3_SHUTTLE_ID)
{
printf("! Warning invalid sensor shuttle. This application will not support this sensor \r\n"
"1.Check the sensor shuttle \r\n"
"2.Reset the board \r\n");
exit(COINES_E_FAILURE);
}
}
init_sensor_interface();
/* after sensor init introduce 200 msec sleep */
coines_delay_msec(200);
init_bmp3();
read_sensor_data();
coines_close_comm_intf(COINES_COMM_INTF_USB);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;Further reads
Datasheets:
Application notes:
Handling, soldering and mounting instructions
Still looking for something?
- Top Results